VyOS High Availability (HA) Deployment on AWS
This document describes how to deploy VyOS in a High Availability (HA) configuration on AWS using Terraform and a VPC Route Server to provide sub-second failover.
Why Use HA on AWS?
This solution helps organizations achieve high availability routing with dynamic connectivity to multiple AWS VPCs or hybrid environments.
Key Advantages:
Utilizes AWS VPC Route Server to manage BGP routes dynamically.
Deploys two VyOS EC2 instances as BGP peers connected to the Route Server. Although both participate, one is typically preferred as the next-hop.
Employs Bidirectional Forwarding Detection (BFD) for rapid failure detection.
On failure:
Withdraws the failed peer’s routes from the RIB.
Recomputes the optimal path in the FIB.
Updates VPC route tables to point to the active instance.
Enables sub-second failover (< 1 s), outperforming AWS API-based route table failover.
This architecture supports:
Cloud edge routing with failover.
Hybrid cloud resiliency.
Rapid recovery during instance crashes, upgrades, or network disruptions.
Continuity for mission-critical operations.
HA Architecture Diagram
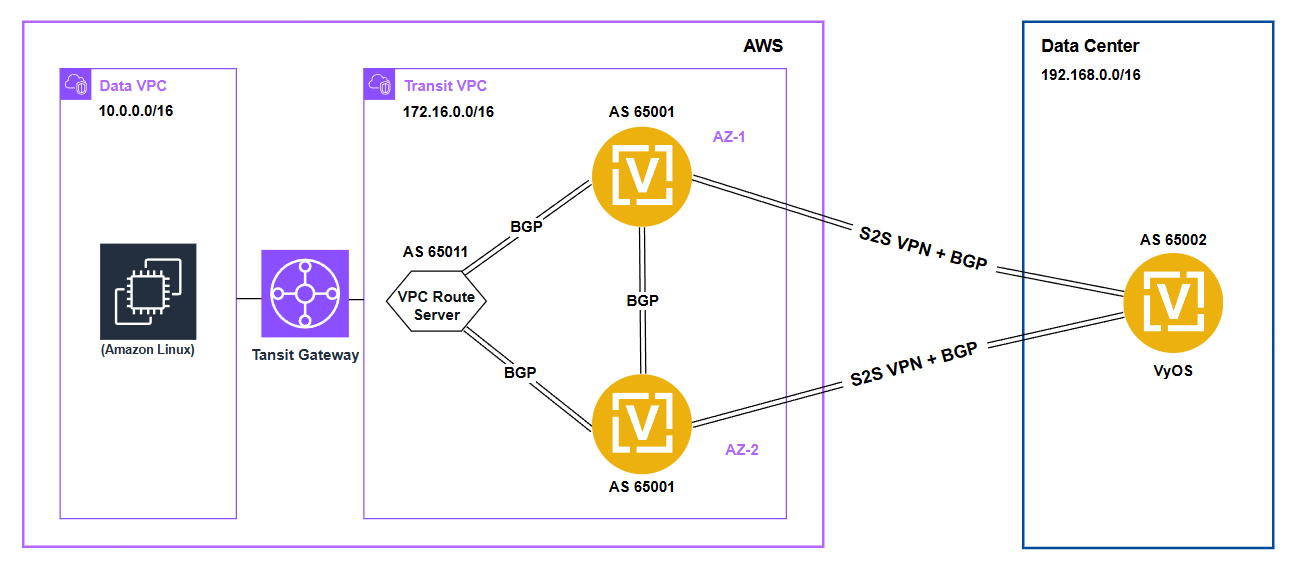
Terraform Automation
To streamline and standardize the process, we developed a Terraform project that automates the deployment of VyOS in High Availability (HA) mode on AWS.
This Terraform project automates the deployment of:
Two VyOS instances in HA mode.
VPC Route Server.
Transit Gateway.
A Transit VPC and a Data VPC containing a test Amazon Linux EC2 instance for connectivity validation.
To integrate with existing AWS infrastructure:
Remove the Data VPC, its subnets, and EC2 test instance.
Update main.tf, network.tf, transit_gateway.tf, variables.tf, and outputs.tf accordingly.
Prerequisites
AWS Environment:
Active AWS account with permissions for EC2, VPC, Transit Gateway, Route Server, and IAM (for keypair and role management).
Local Environment:
AWS CLI installed: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/userguide/getting-started-install.html
Terraform installed: https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/tutorials/aws-get-started/install-cli
Set AWS credentials in your shell:
export AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID="<AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID>"
export AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY="<AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY>"
export AWS_SESSION_TOKEN="<AWS_SESSION_TOKEN>"
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION="<AWS_REGION>" # e.g., us-east-1
Obtain VyOS AMI ID and Owner ID:
Subscribe to VyOS via AWS Marketplace. Then run:
aws ec2 describe-images \
--owners aws-marketplace \
--filters "Name=product-code,Values=8wqdkv3u2b9sa0y73xob2yl90" \
--query 'Images[*].[ImageId,OwnerId,Name]' \
--output table
Alternatively, set the vyos_ami_id variable directly in variables.tf.
Generate an SSH keypair (or use the included demo key):
ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsa -m PEM -f keys/vyos_custom_key.pem
chmod 400 keys/vyos_custom_key.pem
Usage
Configure variables in variables.tf, including instance type, region, and vyos_ami_id.
Terraform Workflow:
terraform init
terraform fmt
terraform validate
terraform plan
terraform apply
On completion, run:
terraform output
This displays the management IP and connectivity test results.
To clean up:
terraform destroy
Management
SSH into VyOS:
ssh vyos@<vyos_public_ip> -i keys/vyos_custom_key.pem
GitHub Repository
You can clone or download the Terraform project and use them in your environment:
https://github.com/vyos/vyos-automation/tree/main/Terraform/AWS/ha-instances-with-configs